
Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam: U.S. Hits Vietnamese Goods with 46% Duty, Prompting Urgent Trade Talks
1. US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam: What Exporters Must Know
The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam policy is creating ripples in global trade. As the U.S. considers implementing this strategy, Vietnamese exporters face serious implications. Understanding this policy and its effects is critical for businesses to adapt and thrive.
1.1 What Is the US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam Policy?
The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam refers to a potential trade mechanism where the U.S. imposes the same tariff rates on Vietnamese goods as Vietnam places on U.S. products. For example, if Vietnam levies a 20% tariff on American cars, the U.S. would impose a 20% tariff on Vietnamese exports in the same category.
1.1.1 Why the US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam Matters
This approach aims to enforce fair trade. However, it introduces uncertainty and may trigger higher tariffs, delays, and additional costs for Vietnamese exporters.
Vietnam has grown its exports rapidly, particularly to the U.S. The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam initiative could disrupt this growth, especially in key sectors such as electronics, textiles, and furniture.
1.2 US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam: Reasons Behind the Policy
The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam concept is partly a response to trade imbalances. The U.S. sees Vietnam's increasing trade surplus as problematic. U.S. policymakers argue that reciprocal action is necessary.
With many U.S. companies relocating from China to Vietnam, the latter has become a major beneficiary. The U.S. wants to ensure that this shift does not result in new trade imbalances.
The U.S. claims some Vietnamese policies give local producers an unfair edge. By implementing the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam, they hope to level the playing field.
1.3 Impact of US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam on Key Export Sectors
Vietnam’s Key Exports to the US, 2024 | ||
Items | Value (US$) | Proportion |
Total | 119,501,485,006 | 100.00% |
Computers, electrical products, spare-parts and components thereof | 23,201,555,610 | 19.42% |
Machine, equipment, tools and instruments | 22,052,523,094 | 18.45% |
Textiles and garments | 16,151,794,382 | 13.52% |
Telephones, mobile phones and parts thereof | 9,824,431,700 | 8.22% |
Wood and wooden products | 9,056,598,490 | 7.58% |
Foot-wears | 8,284,399,219 | 6.93% |
Other products | 8,111,464,983 | 6.79% |
Other means of transportation, parts and accessories thereof | 3,273,825,912 | 2.74% |
Plastic products | 3,081,809,424 | 2.58% |
Fishery products | 1,832,900,465 | 1.53% |
Handbags, purses, suit-cases, headgear and umbrellas | 1,802,632,964 | 1.51% |
Toys and sports requisites; parts and accessories thereof | 1,781,174,208 | 1.49% |
Iron and steel products | 1,331,044,294 | 1.11% |
Iron and steel | 1,318,963,272 | 1.10% |
Still image, video cameras and sparts thereof | 1,208,345,217 | 1.01% |
Cashew nut | 1,154,132,402 | 0.97% |
Source: Vietnam Customs and Vietnam Briefing | ||
Apparel and Textile Industry
Vietnam is the second-largest textile exporter to the U.S. The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam would significantly impact this sector, especially low-cost garment producers.
Electronics and Components
Vietnamese electronics exports could suffer under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam. Tariff hikes on components would increase production costs and reduce global competitiveness.
Furniture and Wood Products
Vietnam is a top furniture exporter to the U.S. The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam policy would hit this low-margin, high-volume sector hard, leading to reduced profits.
Seafood and Agricultural Products
Seafood and farm exports may also face challenges. The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam will likely cause price hikes and potential loss of market share in the U.S.
1.4 How the US Reciprocal Tariff on Vietnam Affects Businesses
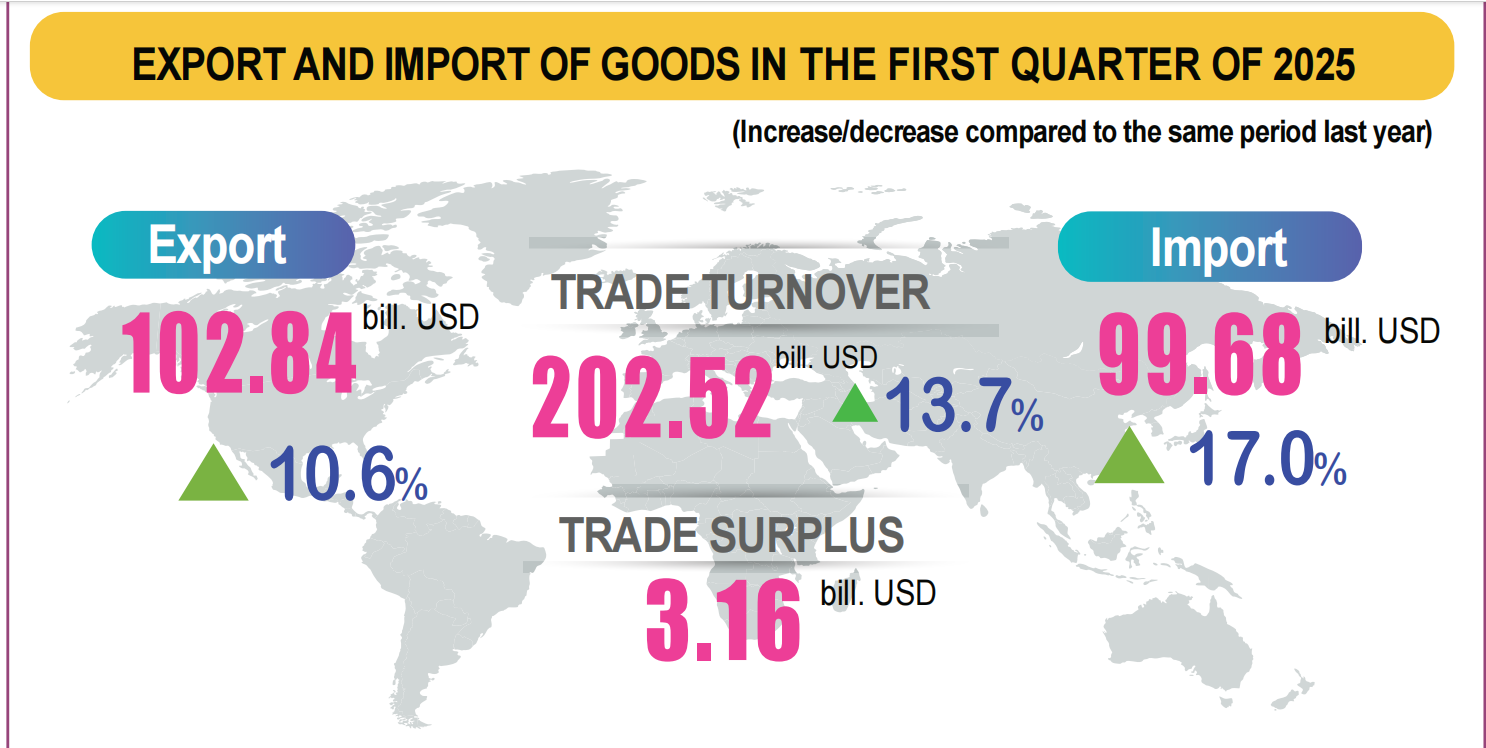
Photo Source Ministry of Finance
Higher Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
With the US reciprocal tariff on Vietnam, costs will rise. Exporters must decide whether to absorb the increase or raise prices—both options involve risk.
Disruption of Supply Chains
Volatile tariffs result in unstable shipping schedules and order cancellations. The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam creates pressure on logistics, forcing firms to adapt quickly.
Contract Adjustments with U.S. Clients
Long-term contracts must be revised to reflect the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam policy. Exporters must negotiate new pricing, delivery, and risk clauses.
Strategic Uncertainty for Investors
The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam introduces unpredictability for foreign investors, potentially slowing future investments in Vietnamese manufacturing.
2. US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam: Exporter Readiness Guide
Vietnamese exporters must act fast. Proactive planning can help businesses survive and thrive under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam scenario.
2.1 Strengthen Compliance and Trade Documentation
Ensure Proper HS Codes
Under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam, accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes are vital. Errors can result in penalties or delays.
Declare Accurate Origins
Exporters must clearly indicate the country of origin. Compliance with the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam rules requires transparent documentation.
Use Certificates of Compliance
Using correct certificates ensures that goods qualify under trade agreements or are not misclassified under US reciprocal tariff Vietnam policies.
2.2 Market Diversification to Reduce Risk
Entering New Markets
Reducing reliance on the U.S. is crucial. Exporters should look to the EU, Japan, and ASEAN markets as buffers against the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam risks.
Leveraging FTAs
Vietnam’s participation in CPTPP and EVFTA allows exporters to enjoy lower tariffs elsewhere. These agreements can offset US reciprocal tariff Vietnam impacts.
2.3 Optimize Logistics and Freight Planning
Consolidate Shipments
To manage US reciprocal tariff Vietnam costs, exporters should consider consolidating shipments to reduce freight expenses.
Choose the Right Incoterms
Reassessing Incoterms can balance risk and cost, especially under US reciprocal tariff Vietnam uncertainty.
Use Flexible Warehousing
Bonded warehouses and FTZs help delay duty payments. These strategies ease financial strain under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam regime.
2.4 Consider Tariff Engineering Strategies
Product Modification
Small changes in product makeup can shift tariff classifications. This method may reduce exposure to US reciprocal tariff Vietnam.
Repackage or Reassemble
Altering packaging or completing final assembly in a third country can influence tariff rates under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam structure.
Legal and Expert Guidance
Tariff engineering must comply with all trade laws. Engage with trade lawyers and experienced logistics partners for US reciprocal tariff Vietnam support.
3. US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam: Logistics as a Strategic Ally
Logistics partners like VICO Logistics play a vital role in navigating the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam environment.
3.1 Scenario Planning for Tariff Outcomes
Logistics experts can forecast how different US reciprocal tariff Vietnam rates will affect cost and delivery.
Based on simulation outcomes, they propose real-world solutions to reduce delays, costs, and risks linked to US reciprocal tariff Vietnam.
3.2 Customs and Tariff Classification Services
Expert Tariff Classification
Proper classification avoids overpayment. Logistics companies ensure Vietnamese goods are accurately placed under US reciprocal tariff Vietnam categories.
Timely Documentation Submission
Fast and correct documentation prevents delays. It’s vital under the strict US reciprocal tariff Vietnam rules.
3.3 Warehousing and Distribution Strategies
Bonded Warehousing
Delaying duties using bonded warehouses helps exporters manage their cash flow amid US reciprocal tariff Vietnam uncertainties.
Multi-Country Inventory Planning
Placing goods in FTZs or nearby countries helps optimize cost under the US reciprocal tariff Vietnam scenario.
Final Thoughts on US Reciprocal Tariff Vietnam
The US reciprocal tariff Vietnam policy is more than a trade tactic—it’s a new reality. Exporters must adapt fast. With careful planning, market diversification, and the right logistics partners, Vietnamese companies can stay resilient and competitive.
Learn more other articles at
1. Vietnam Textile Exports EU: New Demands & Logistics Needs
2. New VAT Policy in Vietnam: Impact on Bonded Warehouses and Logistics Solutions
3. Vietnam Events 2025: Your Gateway to Global Business Opportunities
VICO LOGISTICS – Your Indochina Logistics Expert
Premium member of Eurocham, JCtrans, VLA, VCCI, VITAS, VICOFA... associations
Owned offices: Hong Kong (headquarters), China (Shenzhen, Shanghai), Vietnam (Ho Chi Minh, Da Nang, Hai Phong).
Follow us for more valuable information
Book now: https://vico.com.hk/#quotation
Contact us: mkt4_hcm@vico.com.hk (For business development)






